

 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
|||
 |
 |
||
 |
|||
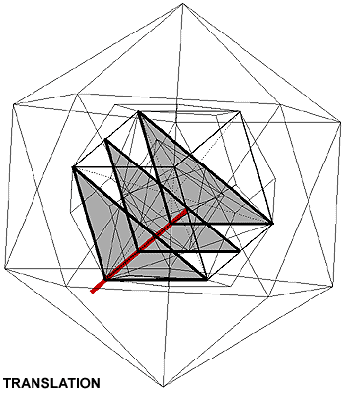
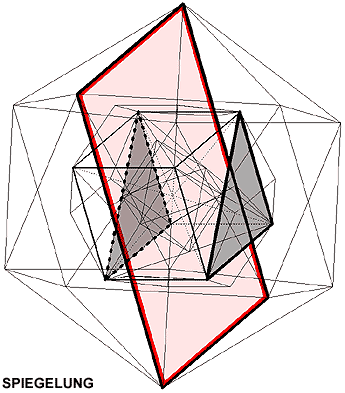
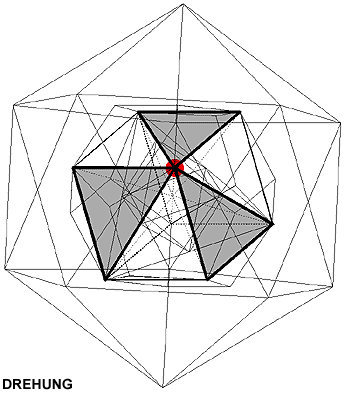
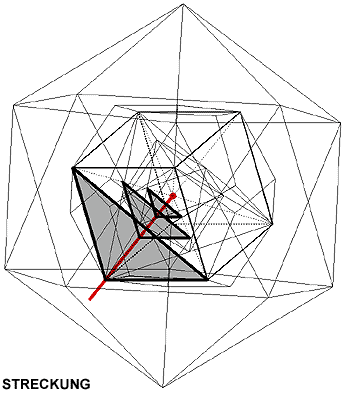
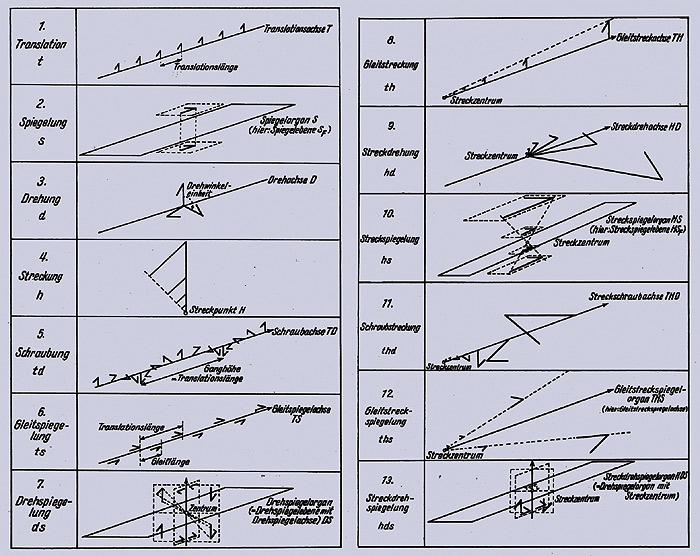
Symmetrical operations are transformations causing a figure to come into line with itself.
Symmetrical organs (in red) are centre, axis or plane, which define symmetrical operations.
Wolf / Wolff make a distinction between thirteen symmetrical formations with point, straight line and surface as symmetrical organs. They are each and all contained in the Metaeder, i.e.:
Translation (T): simple straight-line shift or sliding
Reflection (S): reversed-side image, mirror symmetry
Rotation (D): rotation about an axis, rotational symmetry
Expansion (H): lengthening / stretching (or shortening / curtailment)
and, in addition:
Helicalisation, mirror imaging by sliding, mirror imaging by rotation, slide stretching, stretch rotation, mirror imaging by stretching, stretch helicalisation, mirror imaging by sliding and stretching, mirror imaging by stretching and rotation, turning or inversion