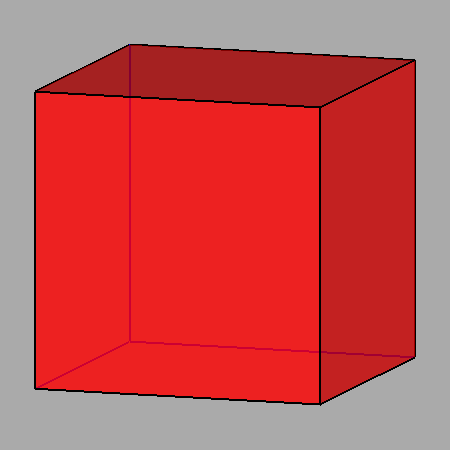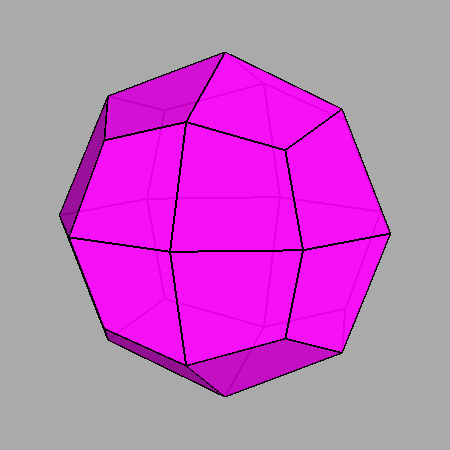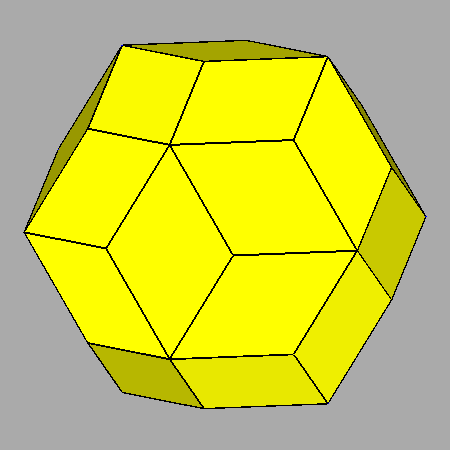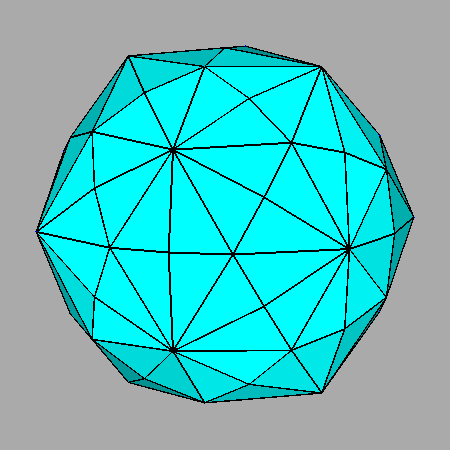
 |
 |
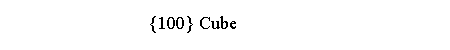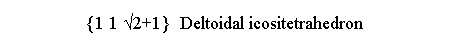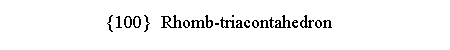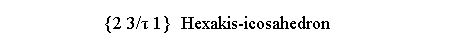 |
 |
|
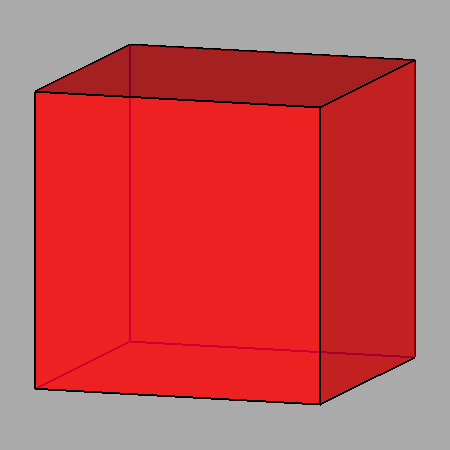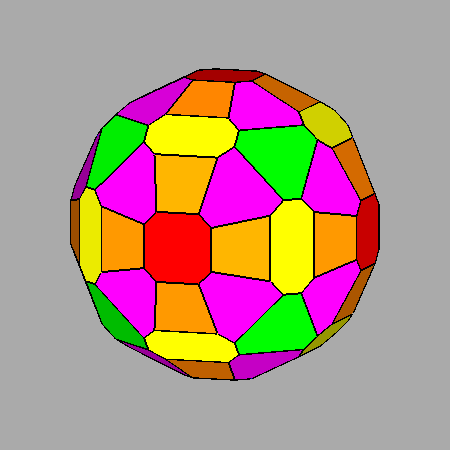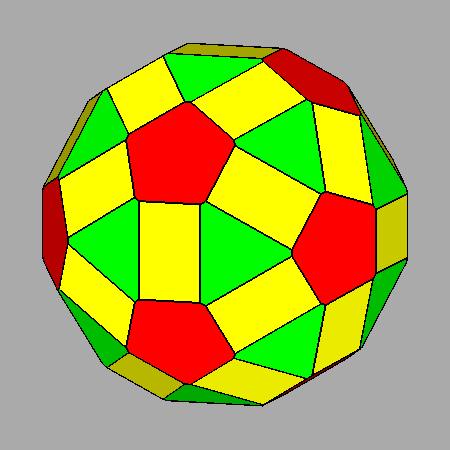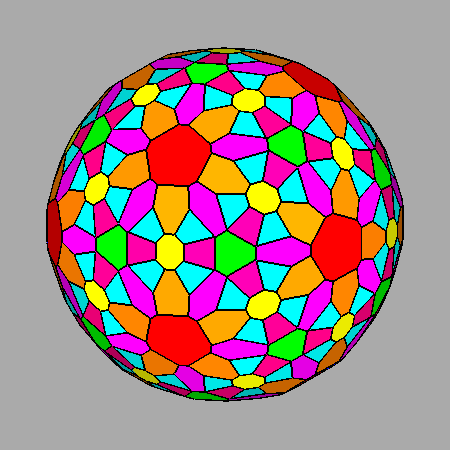
Sequential intersections of the seven forms, corresponding to Platonic and Catalan solids, which characterize both m3m cubic and m 3 5 icosahedral point groups. |
PLATONIC AND CATALAN POLYHEDRA AS ARCHETYPES OF FORMS
BELONGING TO THE CUBIC AND ICOSAHEDRAL SYSTEMS
Livio Zefiro* and Maria Rosa Ardigo'
*Dip.Te.Ris., Universita' di Genova, Italy
 |
 |
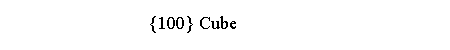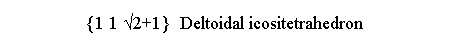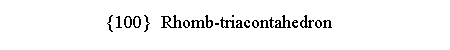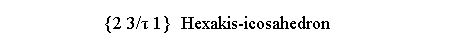 |
 |
|
Sequential intersections of the seven forms, corresponding to Platonic and Catalan solids, which characterize both m3m cubic and m 3 5 icosahedral point groups. |
Notes
|
 PYRITE |
SPHALERITE |
 |
|
Figure 1 - Pleasant examples of cubic natural crystals deriving from the intersection of many single forms, whose name and Miller's indices are displayed hovering with the mouse on every face of the three crystals. |
 |
 |
 |
|
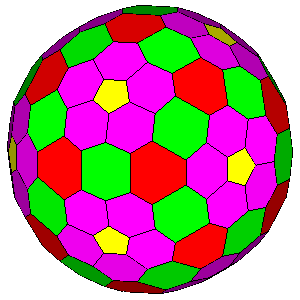
Figure 2 - Composite icosahedral forms belonging to 235 (left) and m 3 5 (right) point groups. The central form is consistent with both point groups. |
Unlike the {hkl} general form, which is different
in the m 3 5
and 235 icosahedral point groups since only the former has mirror planes and inversion centre,
each of the six special forms is shared by the two icosahedral point groups [1].
On the whole, the forms belonging to each icosahedral point group are seven, as many as the forms in each of the five
cubic point groups, which, in general, are more familiar than the icosahedral
ones.
Focusing on the holohedral symmetries, both m3m cubic and
m 3 5 icosahedral point groups include,
in addition to two forms equal to Platonic solids
[2],
each dual of the other (cube and octahedron in
m3m, dodecahedron and
icosahedron in m 3 5),
another form with fixed Miller’s indices, equal to a Catalan solid:
in m3m point group it is the rhomb-dodecahedron {110},
dual of the quasi-regular cuboctahedron,
whereas in m 3 5 it is the rhomb-triacontahedron
{100}, dual of another quasi-regular polyhedron, the icosi-dodecahedron (Figure 3).
|
|
|
|
|
| cube | dodecahedron | rhomb-dodecahedron | rhomb-triacontahedron |
|
|
|
|
|
| octahedron | icosahedron | cuboctahedron | icosi-dodecahedron |
|
Figure 3 - Couples of dual polyhedra made of two
Platonic polyhedra ( 1st and 2nd column), or a Catalan and a quasi-regular polyhedra
(3rd and 4th column). It must be pointed out that a convex
quasi-regular polyhedron is an Archimedean polyhedron in which
each edge is shared by two different faces consisting in regular polygons with
m-
and n-sides.
|
The other four forms belonging to each point group are:
All the forms characterizing the
m 3 5 and m3m
point groups can be compared in Table 1: the correlated icosahedral and cubic forms are shown on the same row.
(It must be pointed out that
m 3 5
and m3m are the
Hermann-Mauguin point group symbols adopted by the International Tables
for Crystallography [1], in the short version; the more explanatory full symbols are
2/m 3 5 and
4/m 3 2/m, respectively).
|
Correlated cubic and icosahedral forms characterizing the m 3 5 and m3m point groups |
|
|
Forms of the m 3 5
icosahedral point group (golden ratio τ = 1.61803...) |
Forms of the m3m cubic point group
(h>k>l) |
| {1τ 0} dodecahedron | {100} cube |
| {111} icosahedron | {111} octahedron |
| {100} rhomb-triacontahedron | {110} rhomb-dodecahedron |
| {hk0} triakis-icosahedron (where: 0 < k/h <1/τ2) | {hhk} triakis-octahedron |
| {hk0} deltoidal hexecontahedron (where: 1/τ < h/k <τ2) | {kkh} deltoidal icositetrahedron |
| {hk0} pentakis-dodecahedron (where: 0 < h/k <1/τ) | {hk0} tetrakis-hexahedron |
| {hkl} hexakis-icosahedron | {hkl} hexakis-octahedron |
|
Table 1 -
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
triakis-icosahedron {τ2+1 1/τ 0} |
deltoidal hexecontahedron {τ+1/τ τ 0} |
pentakis-dodecahedron {1 3τ 0} |
hexakis-icosahedron {2 3/τ 1} |
|
|
|
|
|
| triakis-octahedron {1 1 √2-1} |
deltoidal icositetrahedron {1 1 √2+1} |
tetrakis-hexahedron {210} |
hexakis-octahedron {2√2+1 √2+1 1} |
|
Figure 4 - Further Catalan polyhedra belonging to the m 3 5 icosahedral and m3m cubic point groups (first and second row, respectively) |
 |
|
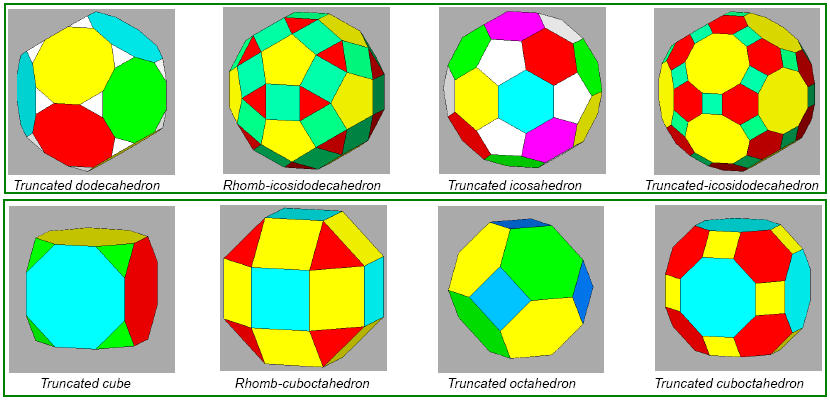
Figure 5 - Semi-regular Archimedean solids, belonging to
the m 3 5
(first row) or m3m
point group (second row), duals of the Catalan solids shown in Figure 4.
|
|
Sets of {hkl} indices relative to the forms, belonging to m 3 5 icosahedral and m3m cubic point groups, which correspond to archetypal Platonic and Catalan polyhedra | |||
|
Icosahedral polyhedra |
Indices {hkl} | Cubic polyhedra | Indices {hkl} |
| Dodecahedron | {1τ 0} | Cube | {100} |
| Icosahedron | {111} {τ 1/τ 0} |
Octahedron | {111} |
| Rhomb-triacontahedron |
{100} {τ 1 1/τ} |
Rhomb-dodecahedron | {110} |
| Pentakis-dodecahedron |
{1/τ 3 0} {τ2 1 2/τ} {τ+1/τ 2 1/τ} |
Tetrakis-hexahedron | {210} |
| Triakis-icosahedron |
{τ+1/τ
1/τ2 0} {τ 2/τ 1} {2 1 1/τ2} |
Triakis-octahedron | {1 1 √2-1} |
| Deltoidal hexecontahedron |
{τ+1/τ
τ 0} {τ2 1/τ 1/τ} {2 1 τ} |
Deltoidal icositetrahedron | {1 1 √2+1} |
| Hexakis-icosahedron |
{τ+2/τ
1/τ2
1/τ2} {τ2 1 2/τ2} {2+1/τ2 τ 1/τ2} {2 3/τ 1} {τ+1/τ 2/τ 1+1/τ2} |
Hexakis-octahedron | {2√2+1 √2+1 1} |
|
Table 2 -
Set of indices of the archetypal Platonic and Catalan forms belonging to m 3 5
and m3m point groups.
The indices of all the faces of the icosahedral polyhedra can be obtained from the cyclic permutation of a unique set of indices only in case of the dodecahedron, whereas the sets of indices are two, three or five in case of the other six forms. (Each set of indices corresponds to one of the forms belonging to the m3 point group, subgroup of m 3 5, in which the icosahedron and the Catalan polyhedra can be decomposed) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
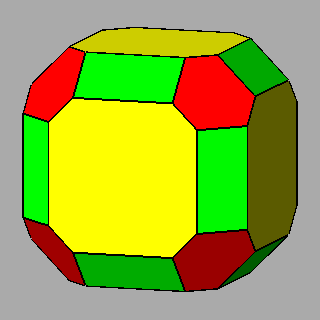 |
|
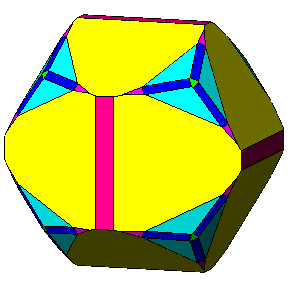
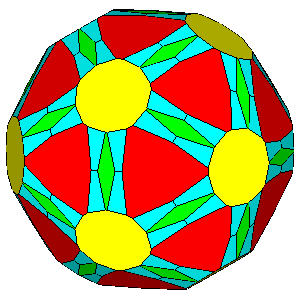
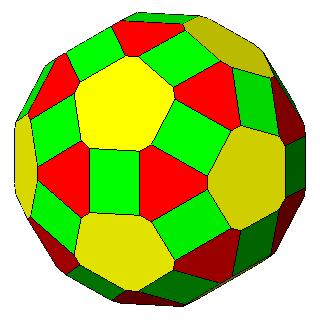
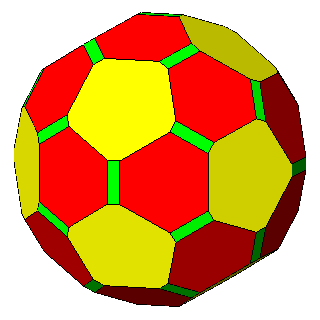
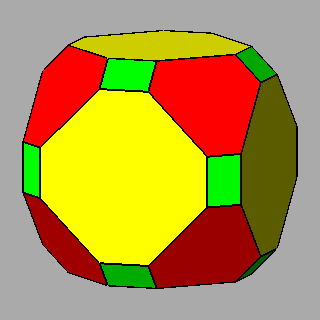
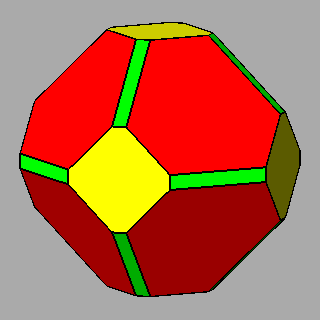
Figure 6 - Forms
of the first subset, given by the intersecton of three single forms
and belonging to the m 3 5
(upper row) or m3m point groups
(lower row), whose vertices are all equivalent by symmetry; their
isohedral duals are generic hexakis-icosahedra or hexakis-octahedra, respectively. |
On the other hand, for particular values of the ratios between the central distances of the faces belonging to the three single forms
(see the
link),
each vertex of the composite form is shared by four faces, consisting
in two rectangles and two regular polygons: they are a triangle and a pentagon
in the m 3 5 point
group (Figure 7a), a triangle and a square in the m 3 5
point group (Figure 8a).
Their dual isohedral polyhedra are deltoidal hexecontahedra or deltoidal icosi-tetrahedra, respectively.
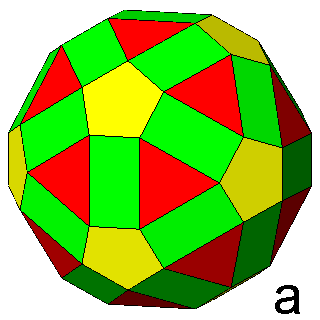 |
 |
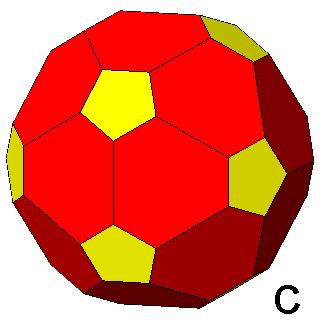 |
|
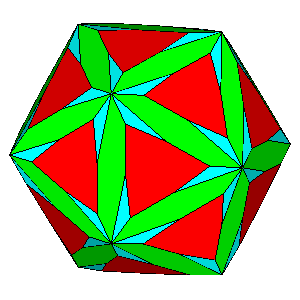
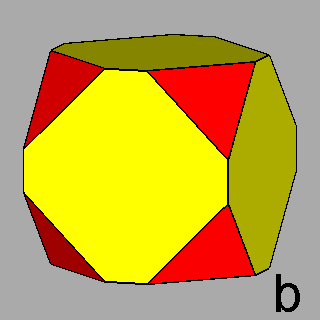
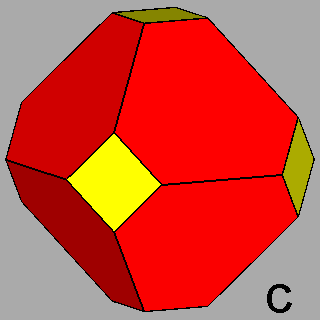
Figure 7 -
Isogonal forms of the first subset, belonging to the icosahedral
system, obtained in case of particular values of the ratio between the central distances of the single forms: |
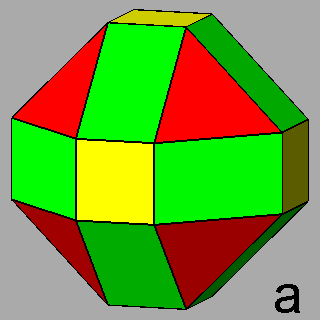 |
 |
 |
|
Figure 8 -
Isogonal forms of the first subset, belonging to the cubic system,
obtained in case of particular values of the ratio between the central distances of the single forms: |
In the absence of the quasi-regular polyhedron (the rhomb-triacontahedron or the rhomb-dodecahedron,
according to the point group), the intersection of the two remaining Platonic solids gives as result,
depending on the ratio between their central distances:
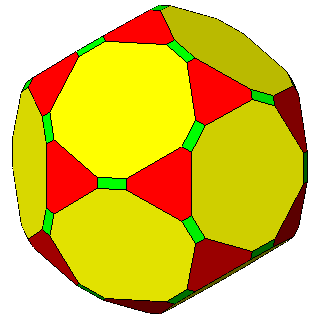
1) in the m 3 5 point group: truncated dodecahedra (Figure 7b),
truncated icosahedra (Figure 7c) and, for the particular ratio
2) in the m3m point group: truncated cubes (Figure 8b), truncated octahedra (Figure 8c) and,
for the particular ratio
Their respective duals are the following polyhedra belonging to the second set:
1) triakis-icosahedra, pentakis-dodecahedra and the rhomb-triacontahedron in the m 3 5
point group
2) triakis-octahedra, tetrakis-hexahedra and the rhomb-dodecahedron in the m3m point group.
It is important to point out that all the isohedral duals belonging to the second set are isomorphic to the archetypal Catalan solids which,
together with the two Platonic polyhedra, characterize both
m 3 5 and m3m point groups.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
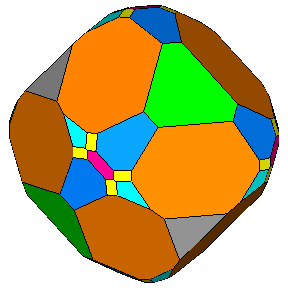
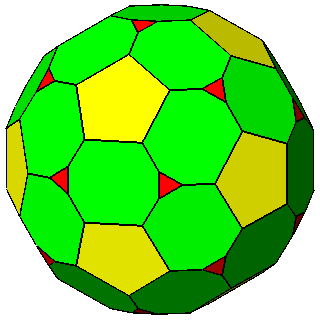
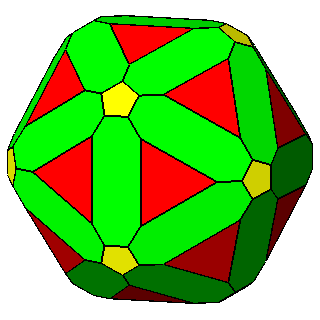
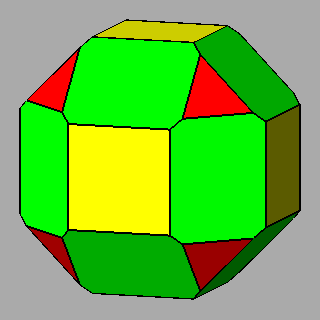
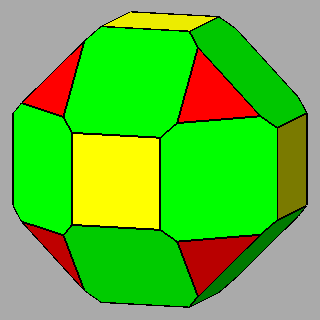
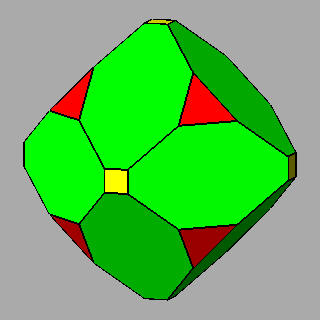
Figure 9 -
Examples of non-isogonal composite forms, belonging to the 2nd subset of the 1st set;
the lengths of the sides of the regular polygons are equal only in the
polyhedra of the central column. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
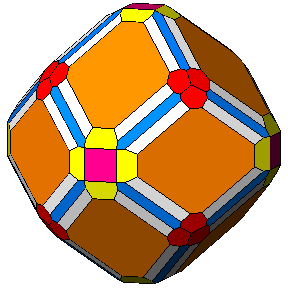
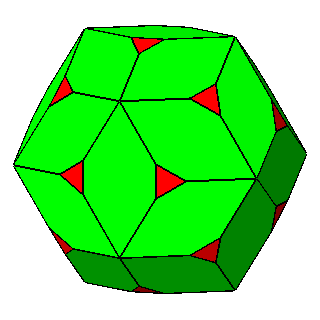
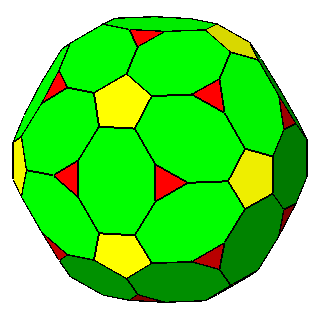
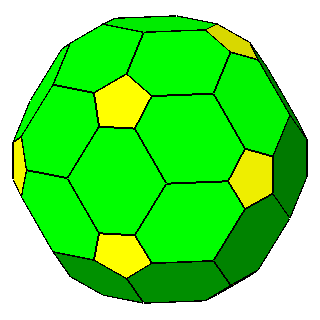
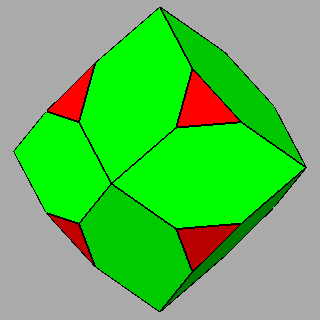
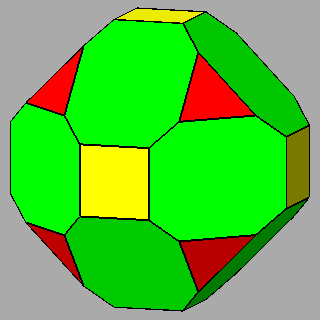
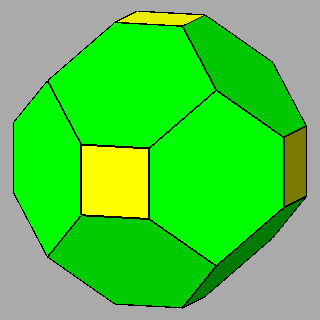
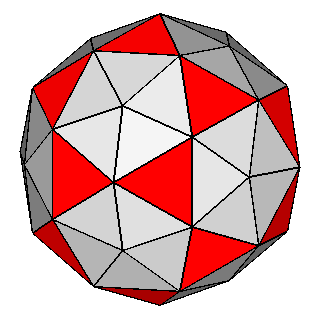
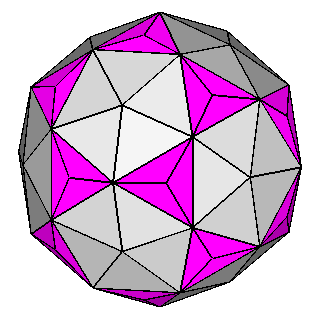
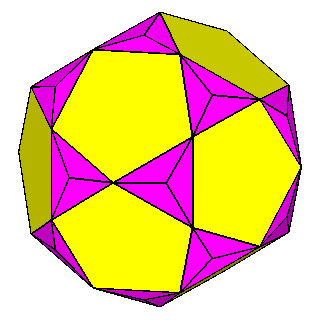
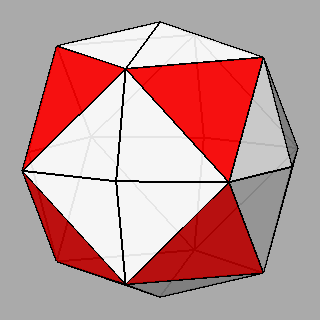
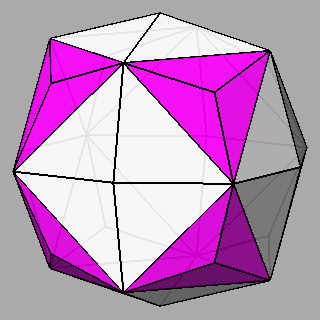
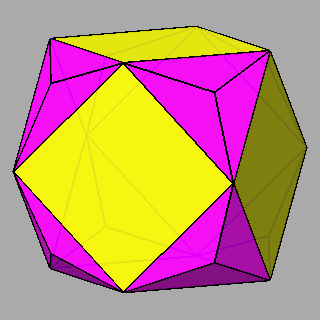
Figure 10 - Non-isogonal polyhedra resulting from the intersection of two forms (in the lateral columns) or three forms (in the central column); their duals are shown in Figure 11. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Figure 11 - Duals of all kinds of non-isogonal composite forms
that belong to the 2nd subset of the first set; depending on the point group which they belong to, they are made of:
One can remark that the forms shown in each row can be also derived from the partial or total augmentation [2] of an icosi-dodecahedron or a cuboctahedron, respectively (the augmentation consists in the erection of a flat pyramid on the pentagonal, square or triangular faces, so that the resulting polyhedron remains convex). |
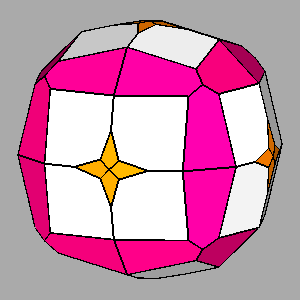
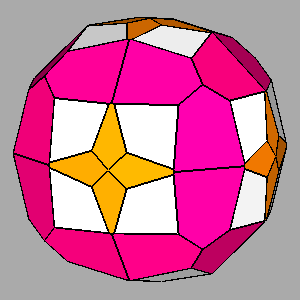
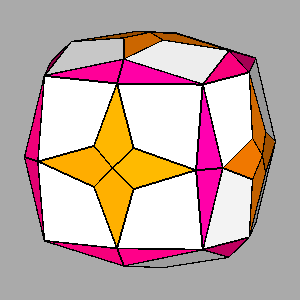
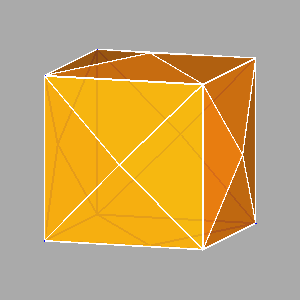
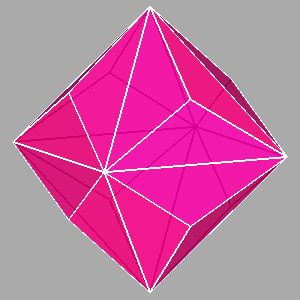
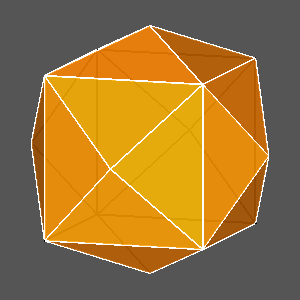
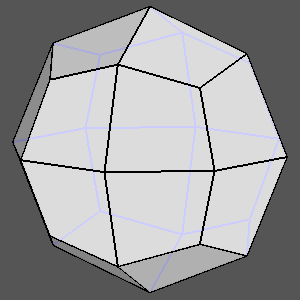
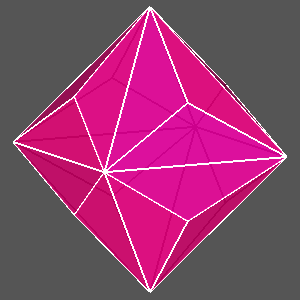
Examples of composite forms belonging to the second set are shown in
Figure 12 and Figure 13.
The first row of both figures reports three composite forms, deriving from the intersection
of the same three single forms: a tetrakis-hexahedron, a deltoidal icosi-tetrahedron and a triakis-octahedron in
m3m, a pentakis-dodecahedron, a deltoidal hexecontahedron and
a triakis-icosahedron in m3 5.
Each image refers to different ratios between the central distances
of the single forms (the faces of the different forms are all equidistant only in the central image).
The archetypes of such three single forms, drawn in
the second row, are their isomorphic Catalan solids, in turn shown in the third row; the fourth row reports the composite forms, resulting from the
intersection of these Catalan solids, to be compared with the composite forms of the first row.
Even if, at a first look, the differences between the corresponding
single forms in the second and third rows are hardly noticeable, the composite forms in the fourth
row, which result from the intersection of the Catalan solids, change
drastically with respect to the composite forms in the first row.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
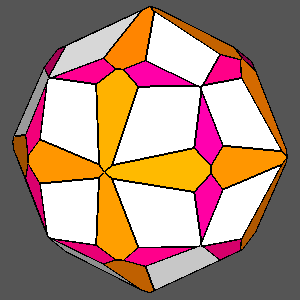 |
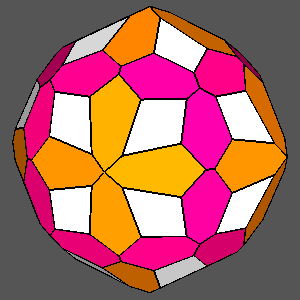 |
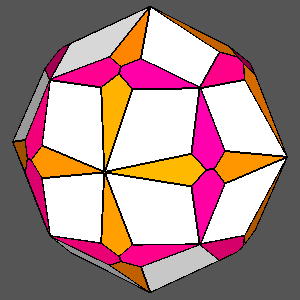 |
|
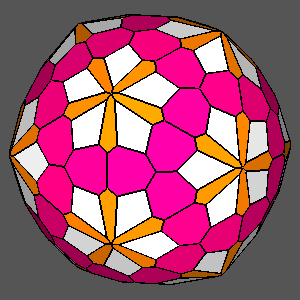
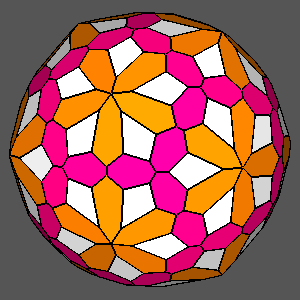
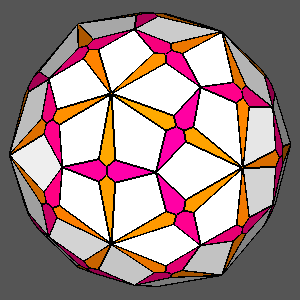
Figure 12
|
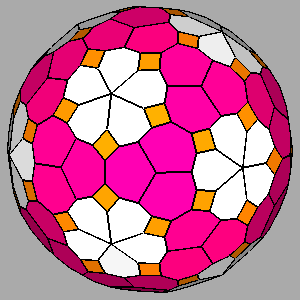 |
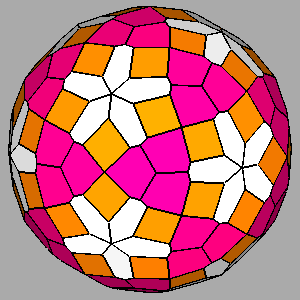 |
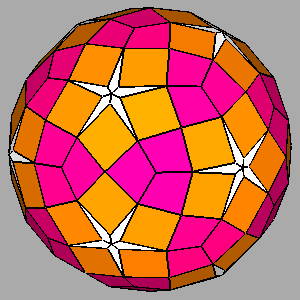 |
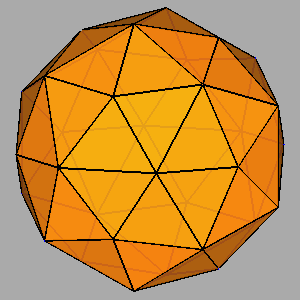 |
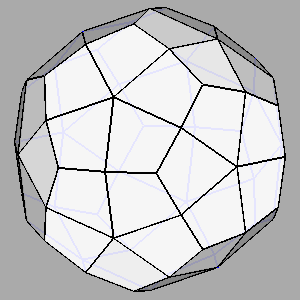 |
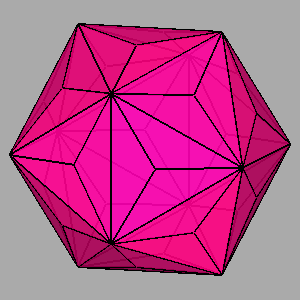 |
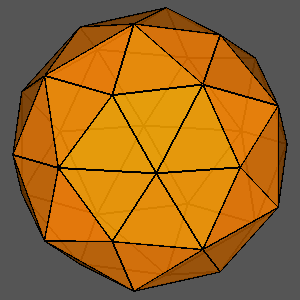 |
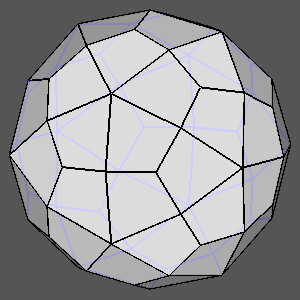 |
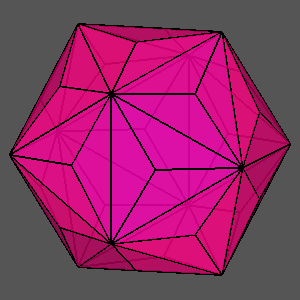 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Figure 13
|
 |
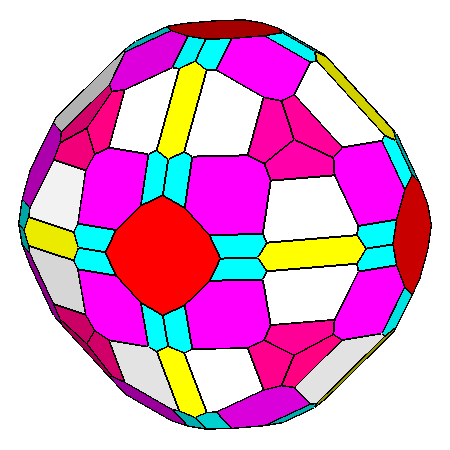 |
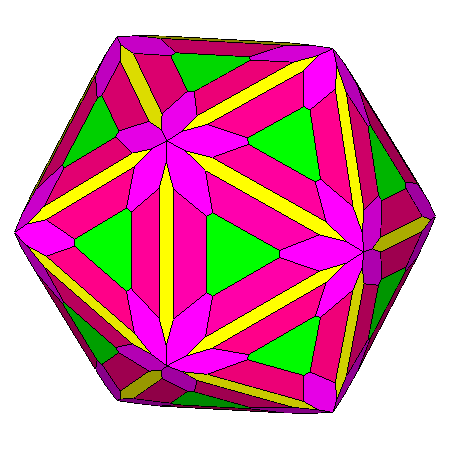 |
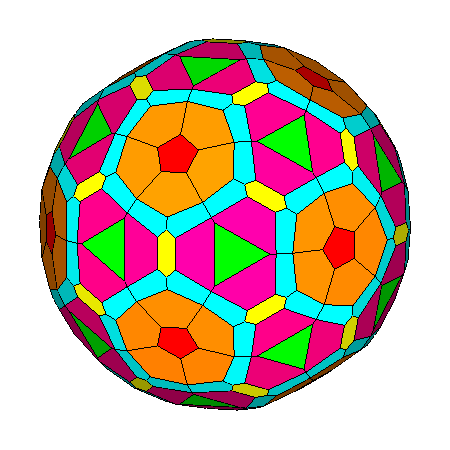 |
|
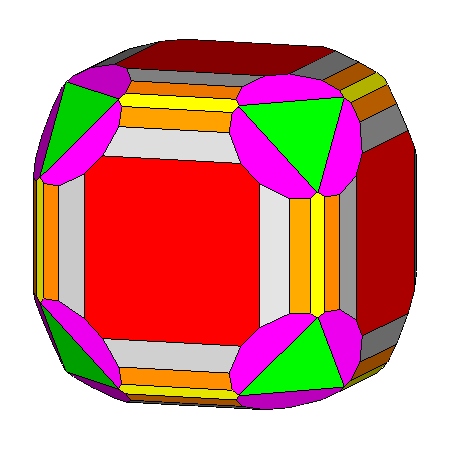
Figure 14
Generic composite polyhedra of the third set, resulting from
the intersection of forms belonging to m3m cubic point group
or m 3 5 icosahedral point group.
The single forms generating the composite forms are: In m3m point group (upper row) In m 3 5 point group (lower row) |
_tC&3x8.png) |
_tD&3x20.png) |
_dual_tC&3x8.png) |
_dual_tD&3x20.png) |
|
Figure 15
(Upper row) Composite polyhedra resulting from
the intersection of an Archimedean solid and its Catalan dual: The vertices are all equidistant from the centre, in case of appropriate ratios between the central distances of the faces. (Lower row) Duals of the composite polyhedra reported in the upper row, consisting of: In each dual, all the faces have the same central distance. |
_tO&4x6.png) |
_tI&5x12.png) |
_dual_tO&4x6.png) |
_dual_tI&5x12.png) |
|
Figure 16
(Upper row) Composite polyhedra resulting from
the intersection of an Archimedean solid and its Catalan dual:
(Lower row) Duals of the composite polyhedra drawn in the upper row, consisting of: |
_RCO&trapezohedron.png) |
_rid&deltoid-hexecontahedron.png) |
_dual_RCO&trapezohedron.png) |
_dual_rid&deltoid-hexecontahedron.png) |
|
Figure 17
(Upper row) Composite polyhedra resulting from
the intersection of an Archimedean solid and its Catalan dual: (Lower row) Duals of the composite polyhedra drawn in the upper row, consisting of: Therefore both these duals belong to the second set previously defined. |
_tCO&6x8.png) |
_tid&hexakisicosahedron.png)
|
_dual_tCO&6x8.png) |
_dual_tid&hexakisicosahedron.png) |
|
Figure 18
(Upper row)
Composite polyhedra resulting from
the intersection of an Archimedean solid and its Catalan dual: (Lower row) Duals of the composite polyhedra drawn in the upper row, consisting of: Therefore also these duals belong to the second set. |
|
Figure 19
Lower row: {112} deltoidal icosi-tetrahedron (on the left) and {τ10} deltoidal hexecontahedron (on the right); they are the isohedral duals of the isogonal polyhedra shown in the upper row. |
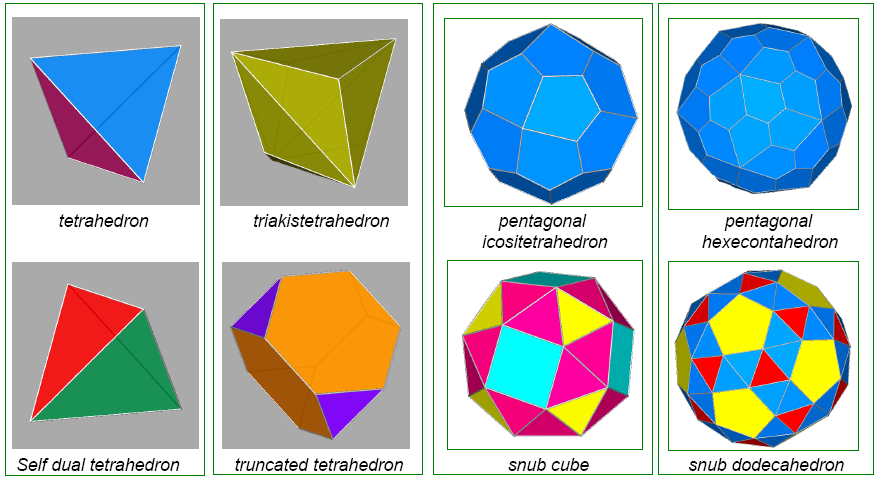 |
|
Figure 20 - Self-dual Platonic
tetrahedra (1st column) and, in the other three columns, the remaining Catalan and Archimedean
dual polyhedra: triakis-tetrahedron and truncated tetrahedron
(2nd column), pentagonal
icosi-tetrahedron and snub cube (3rd column), pentagonal hexecontahedron and snub dodecahedron
(4th column). |
 |
 |
|
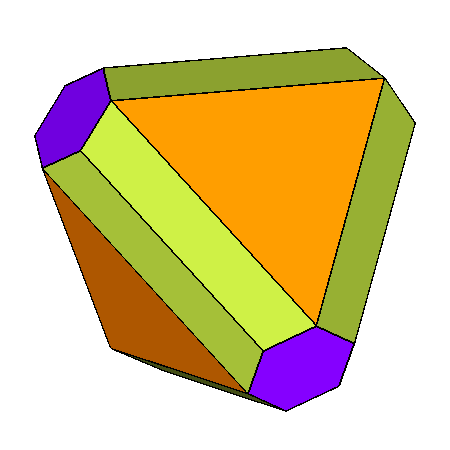
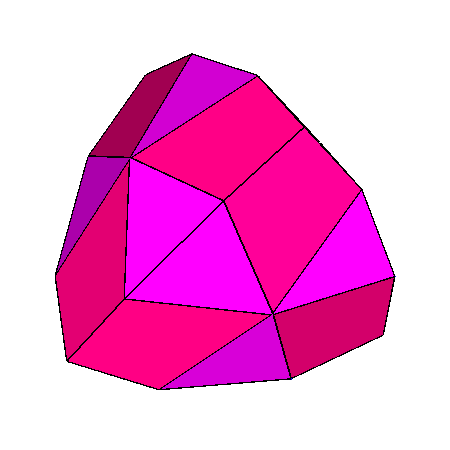
Figure 21
|
 |
 |
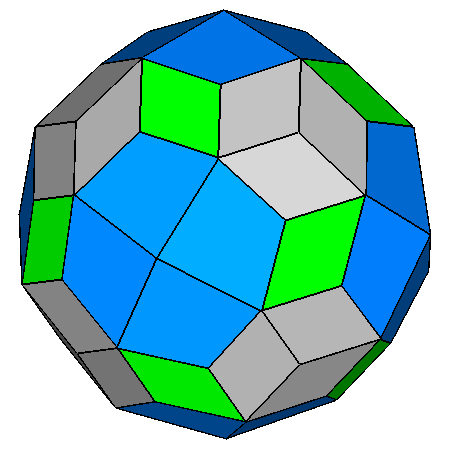 |
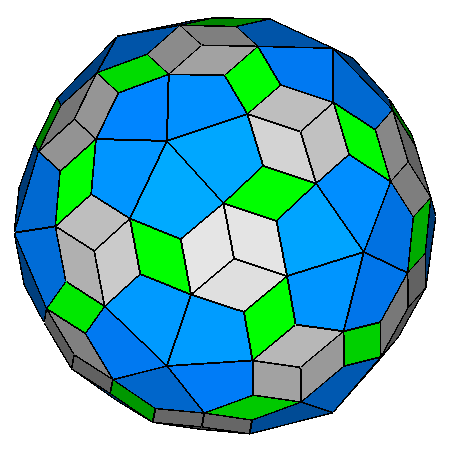 |
|
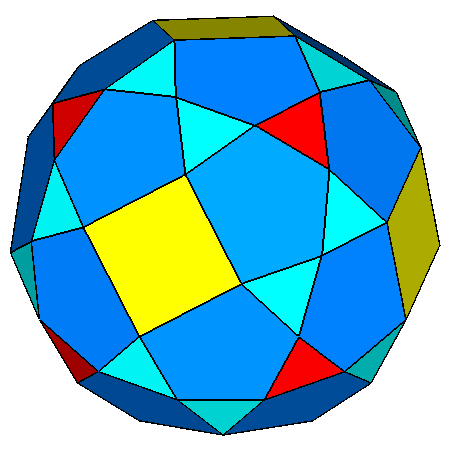
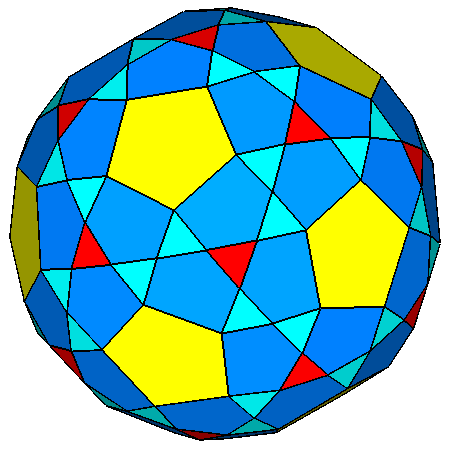
Figure 22
|
In Table 3 the features of all the Platonic and Catalan solids, archetypes of
the cubic and icosahedral single forms, are listed and compared with the
features of the dual Platonic and Archimedean solids.
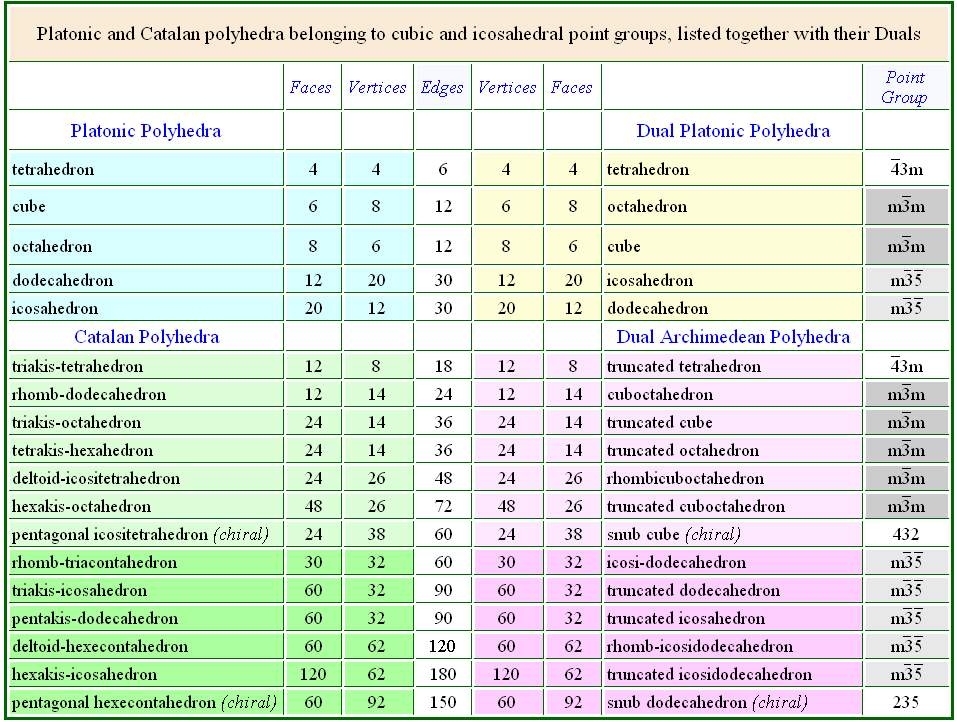
|
| Table 3 - Faces, vertices and edges in Platonic, Catalan and Archimedean polyhedra. |
From the comparison of Table 4 and Table 5 one can ascertain
that the faces of the cubic and icosahedral forms corresponding to Catalan polyhedra have, in pairs,
analogous shapes (the only unpaired Catalan polyhedron is the triakis-tetrahedron):
they differ only in the values of the geometrical parameters.
|
Catalan polyhedra |
Shape of the faces | Geometry of the faces | Angles between the sides of each polygon |
| Triakis-tetrahedron | isosceles triangle |
L1/ L2 = 0.532 Height of the triangular pyramids = 0.163L2 |
2x 33.56° 1x 112.88° |
| Rhomb-dodecahedron | rhombus | Ratio of the diagonals = √2 = 1.414 |
2x 109.47° |
| Tetrakis-hexahedron | isosceles triangle |
L1 / L2
= 3/4 Height of the tetragonal pyramids = L2 / 4 |
2x 48.19° 1x 83.62° |
| Triakis-octahedron | isosceles triangle |
L1/ L2 = 0.586 Height of the triangular pyramids = 0.099L2 |
2x 31.40° 1x 117.20° |
| Deltoidal icositetrahedron | deltoid (or kite) | L1/ L2 = 1.293 |
3x 81.58° 1x 115.26° |
| Hexakis-octahedron | scalene triangle |
L1/ L2 = 1.219 L1/ L3 = 1.631 |
1x 87.20° 1x 55.03° 1x 37.78° |
| Pentagonal icositetrahedron | non-regular symmetric pentagon with 2 equal long sides and 3 equal short sides |
L1/ L2 = 1.420 |
4x 114.81° 1x 80.75° |
|
Table 4 -
List of the cubic Catalan polyhedra,
shape and geometrical parameters of their faces, including the angles between the sides
Li of each polygon.
|
|
Catalan polyhedra |
Shape of the faces | Geometry of the faces | Angles between the sides of each polygon |
| Rhomb-triacontahedron | rhombus | Ratio of the diagonals = τ = 1.618 |
2x 116.565° 2x 63.435° |
| Pentakis-dodecahedron | isosceles triangle |
L1/L2 = 0.887 Height of the pentagonal pyramids = 0.251L2 |
2x 55.69° 1x 68.62° |
| Triakis-icosahedron | isosceles triangle |
L1/L2 = 0.580 Height of the triangular pyramids = 0.057L2 |
2x 30.48° 1x 19.04° |
| Deltoidal hexecontahedron | deltoid (or kite) | L1/L2 = 1+ τ/3 = 1.539 | 2x 86.97° 1x 118.27° 1x 67.78° |
| Hexakis-icosahedron | scalene triangle |
L1/L2
= (2/3)(5-2τ)
= 1.176 L2/L3 = (3/5)τ2 = 1.571 L1/L3 = (2/5)(τ+3) = 1.847 |
1x 88.99° 1x 58.24° 1x 32.77° |
| Pentagonal hexecontahedron | non-regular symmetric pentagon with 2 equal long sides and 3 equal short sides |
L1/L2 = 1.750 | 4x 118.14° 1x 67.44° |
|
Table 5 - List of the icosahedral Catalan polyhedra, shape and geometrical parameters
of their faces, including the angles between the sides Li of each polygon. |
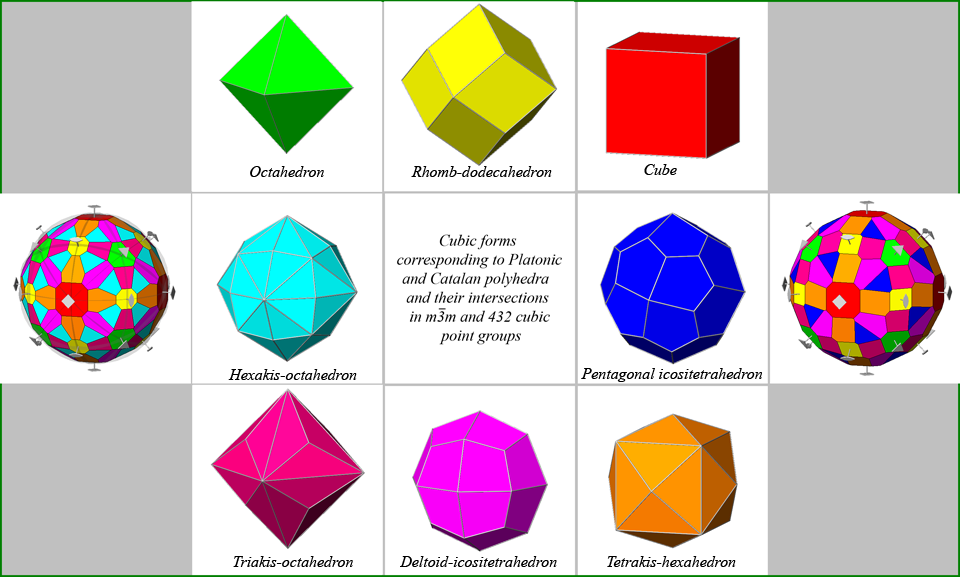
Figure 23 -
Composite forms (symmetry elements included) resulting from the
intersection, in m3m and 432 cubic point groups, of the
equidistant faces belonging to the two Platonic and to the five Catalan polyhedra, archetypes of the
relative isomorphic forms. |
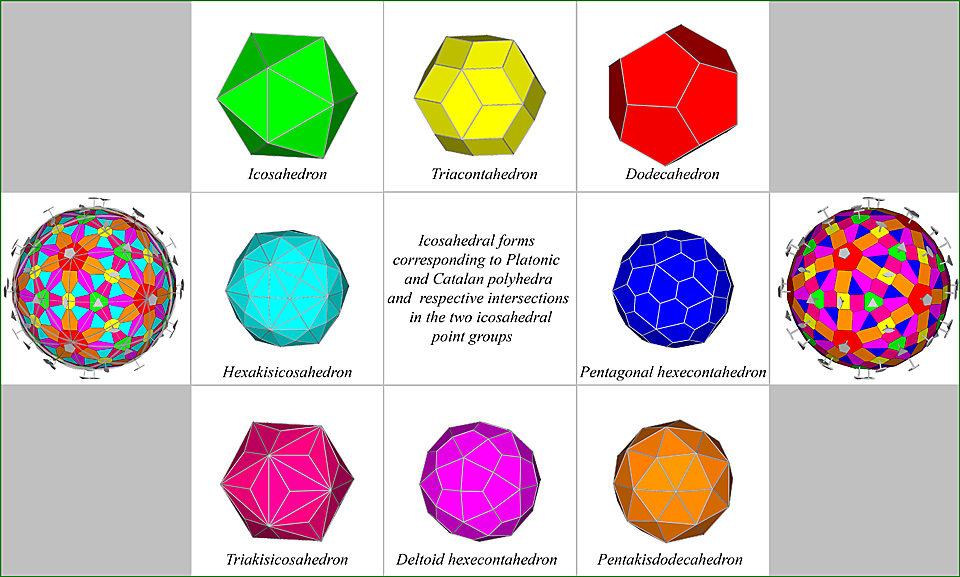
Figure 24 - Composite forms (symmetry elements included) resulting from the intersection, in m 3 5 and
235 icosahedral point groups,
of the equidistant faces belonging to the two Platonic and to the five Catalan polyhedra, archetypes of the
relative isomorphic forms. |