

: Digits Factorial Sum Process.
: Curious Properties of Reiterated
: The Digit Sum Process
Theorem 7.
Let K=5000, then for any non-negative integer n such that 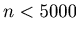 the sequence
the sequence
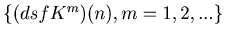 eventually enters into one of the following 8 loops.
eventually enters into one of the following 8 loops.
(1) loop1A ={1} with the length of 1, i.e., a fixed point.
(2) loop1B ={1255} with the length of 1.
(3) loop1C ={2228} with the length of 1.
(4) loop1D ={3366} with the length of 1.
(5) loop1E ={3435} with the length of 1.
(6) loop3 ={13,28,2220} with the length of 3.
(7) loop8 ={16,1657,3325,3183,2271,3552,1281,2222} with the length of 8.
(8) loop12 ={56,4781,1016,1659,271,3548,624,1916,2147,3804,2500,3131}
with the length of 12.
Remark.loop1A,loop1B,loop1C,loop1D and loop1E are so called fixed points.
Proof.
To prove this theorem we are going to use the Mathematica function in Example10.13.
Example 8.1.
loop1A, loop1B, loop1C, loop1D, loop1E are fixed points. Here we present
loop3, loop8 and loop12 as Graph 8.1, Graph 8.2 and Graph 8.3.
Example 8.2.
If we apply dsf5000 function to the number 2288, then in 53 steps the sequence enters into a loop. This is the longest steps for a number to enter into a loop with dsf5000 function. See Graph 8.4.


: Digits Factorial Sum Process.
: Curious Properties of Reiterated
: The Digit Sum Process
![\includegraphics[height=6.8cm]{dsfloopk3.eps}](img169.gif)
![\includegraphics[height=6.8cm]{dsfloopk8.eps}](img170.gif)
![\includegraphics[height=6.8cm]{dsfloopk12.eps}](img171.gif)
![\includegraphics[height=6.8cm]{longeststep5000.eps}](img172.gif)